Difference Between Duct and Gland
Duct and gland are involved in the secretion and production of chemical substances, which mediate the functions of the body. The two types of glands are endocrine glands and exocrine glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands whereas exocrine glands consist of ducts. The main difference between duct and gland is that a duct provides passage to the secretions of the exocrine glands whereas a gland is a secretary organ of the body of plants or animals. Endocrine glands secrete hormones to the blood and exocrine glands secrete enzymes to the target organs through ducts. The exocrine glands such as salivary glands, liver, and pancreas consist of ducts.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is a Duct
– Definition, Types, Secretions, Functions
2. What is a Gland
– Definition, Types, Secretions, Functions
3. What are the Similarities Between Duct and Gland
– Outline of Common Features
4. What is the Difference Between Duct and Gland
– Comparison of Key Differences
Key Terms: Acinus, Adrenal gland, Duct, Endocrine Gland, Exocrine Gland, Hypothalamus, Pituitary gland, Salivary Gland

What is a Duct
A duct is a passage with well-defined walls, which can be used to transport excretions or secretions. This tube-like structure is formed by a row of elongated cells. These elongated cells lack intervening cell walls. Only exocrine glands consist of ducts. A duct starts from an acinus, which produces the secretion. The epithelium of a duct is thicker. Three types of ducts can be found based on the type of epithelium that forms the duct. They are the intralobular duct, interlobular duct, and interlobar duct. The intralobular ducts are formed by the simple cuboidal epithelium and are surrounded by parenchyma cells. The interlobular ducts are formed by the simple columnar epithelium and are surrounded by the connective tissue. The interlobar ducts are formed by the stratified columnar epithelium and are surrounded by connective tissue. Examples of ducts and their secretions are shown in table 1.
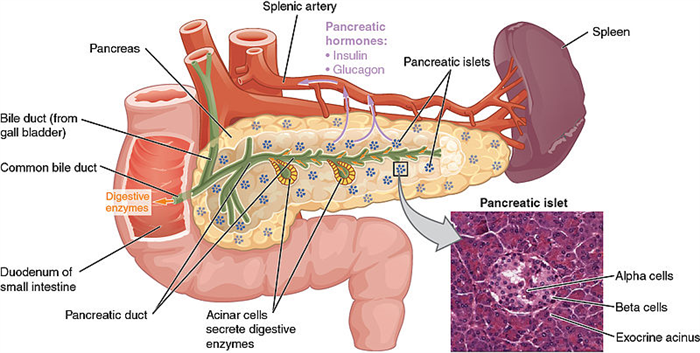
Figure 1: Ducts in the Pancreas
Types of Ducts and their Secretions
Carries bile from the gallbladder to the common bile duct
Carries bile from the liver to the common bile duct
Carries bile from cystic and the common hepatic ducts to the pancreatic duct
Carries bile and pancreatic enzymes from the pancreas to the hepatopancreatic ampulla
Carries milk from the mammary gland to the nipple
Parotid/Submandibular/Major sublingual duct
Carries saliva from the parotid/Submandibular/Major sublingual gland to the mouth
Carries semen from vas deferens to the urethra
What is a Gland
A gland is a secreting organ in the body of either plants or animals. A gland is made up of a specialized type of cells in the epithelial tissue. Glands remove materials from the blood in a selective manner and alter and concentrate the materials in the acinus. These materials are secreted either for further use of the body or for excretion. Glands are made up of either simple cuboidal or columnar epithelium. The two types of glands in the animal body are exocrine glands and endocrine glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands that produce hormones and secrete them into the blood for the transportation to the target organ. Exocrine glands produce enzymes and secrete the enzymes to the target through a duct.
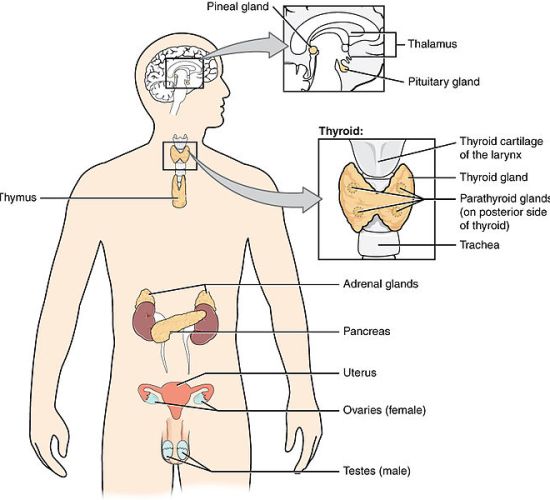
Figure 2: Endocrine Glands
The pituitary gland, hypothalamus, parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and gonads are endocrine glands. The salivary glands, pancreas, and the liver are exocrine glands. The endocrine glands in humans are shown in figure 2.
Similarities Between Duct and Gland
- Both duct and gland are the components of the exocrine glands.
- Both duct and gland are made up of simple cuboidal or columnar epithelium.
- Animal ducts and glands are surrounded by connective tissue while plant ducts and glands are surrounded by parenchyma cells.
- Both duct and gland are involved in the secretion of enzymes to the target organs.
Difference Between Duct and Gland
Definition
Duct: A duct is a passage with cell defined walls, which can be used for either secretions or excretions.
Gland: A gland is a secreting organ in both plants and animals.
Component
Duct: Duct is a component of exocrine glands.
Gland: Gland is a component of both exocrine and endocrine glands.
Found in
Duct: Ducts can be found in liver, pancreas, and salivary glands.
Gland: Glands can be found in endocrine glands such as pituitary glands, thyroid glands, adrenal glands, and in exocrine glands such as salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Function
Duct: Ducts transfer substances produced by glands to the target organ.
Gland: Glands produce secretions.
Conclusion
Duct and gland are the two components of the exocrine glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands. Both ducts and glands are made up of simple cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium. The acinus of the gland produces the secretions of the gland and the secretions are released to the target organ through the duct. The main difference between duct and gland is their function in the body.
Reference:
1. “Duct (anatomy).” Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 09 Aug. 2017. Web. Available here. 13 Aug. 2017.
2. “Gland.” Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., n.d. Web. Available here. 13 Aug. 2017.
Image Courtesy:
1. “1820 The Pancreas” By OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. Jun 19, 2013. (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “1801 The Endocrine System” By OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. Jun 19, 2013. (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
About the Author: Lakna
Lakna, a graduate in Molecular Biology & Biochemistry, is a Molecular Biologist and has a broad and keen interest in the discovery of nature related things