14.1: Structures of the Endocrine System
- OpenStax
- OpenStax
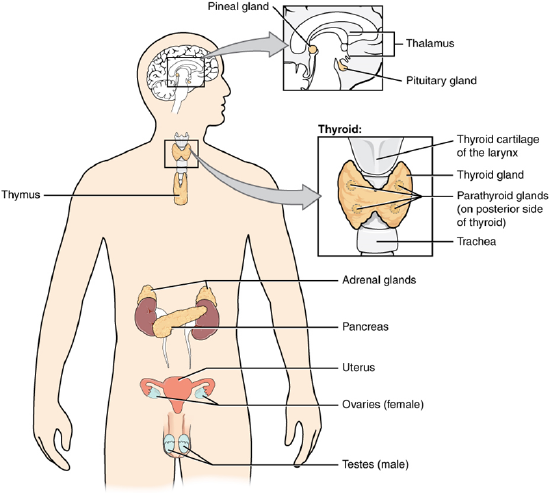
The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones as a primary or secondary function. The endocrine gland is the major player in this system. The primary function of these ductless glands is to secrete their hormones directly into the surrounding fluid. The interstitial fluid and the blood vessels then transport the hormones throughout the body. The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands (Figure \(\PageIndex\)). Some of these glands have both endocrine and non-endocrine functions. For example, the pancreas contains cells that function in digestion as well as cells that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood glucose levels. The hypothalamus, thymus, heart, kidneys, stomach, small intestine, liver, skin, female ovaries, and male testes are other organs that contain cells with endocrine function. Moreover, adipose tissue has long been known to produce hormones, and recent research has revealed that even bone tissue has endocrine functions. The ductless endocrine glands are not to be confused with the body’s exocrine system, whose glands release their secretions through ducts. Examples of exocrine glands include the sebaceous and sweat glands of the skin. As just noted, the pancreas also has an exocrine function: most of its cells secrete pancreatic juice through the pancreatic and accessory ducts to the lumen of the small intestine
This page titled 14.1: Structures of the Endocrine System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax.