Brent Cornell
Exocrine glands produce and secrete substances via a duct onto an epithelial surface – either:
- Salivary glands – secrete saliva which contains amylase (breaks down starch)
- Gastric glands – secretes gastric juices which includes hydrochloric acid and proteases (breaks down protein)
- Pancreatic glands – secretes pancreatic juices which include lipase, protease and amylase
- Intestinal glands – secretes intestinal juices via crypts of Lieberkuhn in the intestinal wall
• Identification of exocrine gland cells that secrete digestive juices from electron micrographs
Exocrine glands are composed of a cluster of secretory cells which collectively form an acinus (plural = acini)
- The acini are surrounded by a basement membrane and are held together by tight junctions between secretory cells
- The secretory cells possess a highly developed ER and golgi network for material secretion and are rich in mitochondria
Exocrine products are released (via secretory vesicles) into a duct, which connects to an epithelial surface
Structure of a Typical Exocrine Gland
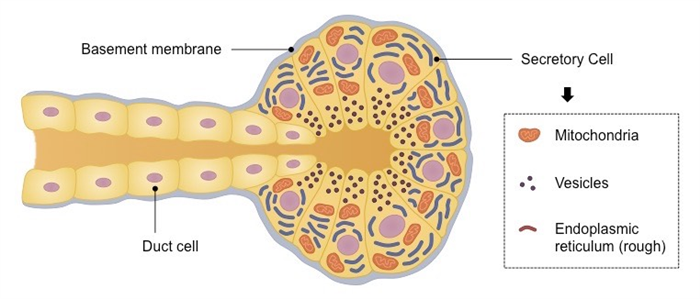
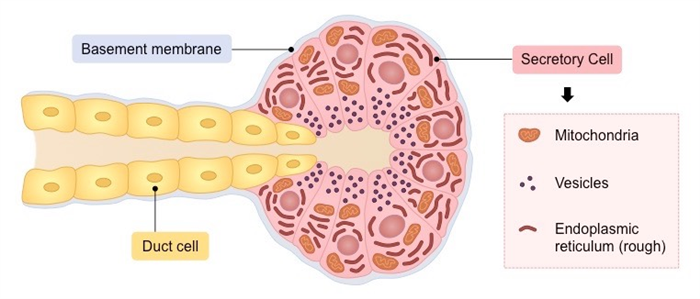
⇒ Click on the image to contrast gland features – acinus ( red ) and duct ( yellow )
Electron Micrograph of an Exocrine Gland
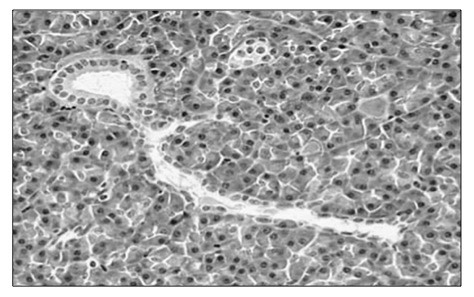
⇒ Click on the image to show false colour representation