Endocrine System: Definition, Parts & Function
Learn the endocrine system definition. Understand the functions of the endocrine system. Learn how does the endocrine system work and what does it regulate.
Table of Contents
What are the 8 functions of the endocrine system?
There are several key functions of the endocrine system, and eight of them include: sleep, sexual development, growth, digestion, regulating sugar levels, metabolism, blood pressure, and heart rate.
What does the term “endocrine system” mean?
‘Endocrine’ is the medical term for an organ that secretes internally, such as all the organs of the endocrine system.
Endocrine System Definition
The endocrine system is a network consisting of glands that produce and secrete hormones internally, since ”endocrine” is a medical term describing organs that secrete internally. A gland is an organ that can produce and release hormones, which are chemicals that travel to organs, skin, other tissues, and muscles in the body. The endocrine system is very important in controlling and regulating several functions throughout the body.
The endocrine system, a complex network of glands with several key functions
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Defining the Endocrine System
Teenagers aren’t the only ones with hormones. And hormones don’t just cause mood swings.
The hormones of your endocrine system help to regulate your energy levels, growth, emotions and ability to reproduce. Hormone-producing glands make up your endocrine system. Hormones are chemicals that your body produces to tell your cells how to behave. They can regulate growth and energy consumption.
Your thyroid gland is in your neck. Your thyroid regulates your metabolism, or how fast your body uses energy. Low levels of thyroid hormones may make you feel tired and lead to weight gain. But, if you have a hyperactive thyroid, your heart may race and you may feel jittery and have trouble falling asleep.
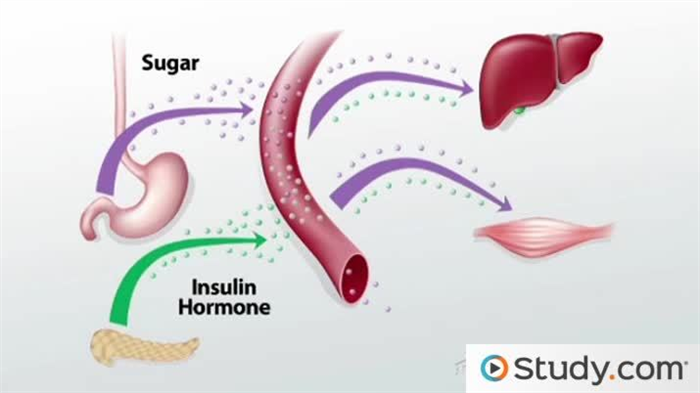
Your pancreas is a gland in your belly that also affects your energy levels. Your thyroid controls the rate at which your body uses energy, and your pancreas regulates how much energy your body gets. Your pancreas produces insulin , the hormone that helps your body absorb sugar in your bloodstream to give it energy. You feel sluggish in the morning when you have low blood sugar. Once you eat breakfast, sugar from the food is carried by your blood. Insulin from your pancreas helps your cells take in the sugar that fuels your body.
In your belly, you also have adrenal glands, which rest on top of your kidneys. Your adrenal glands pump out adrenaline hormones when you’re faced with stress or excited. Say you’re driving, and suddenly see a baby in the road. Your nervous system sends signals to the glands in your endocrine system to put your reactions in motion. Your adrenal glands in your endocrine system release adrenaline to trigger a reaction. You get scared and react quickly as you slam on the brakes. You laugh when you realize it was just a doll that someone lost!
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson
As a member, you’ll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed. Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons. Try it now
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You’re on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. Are you still watching?
- 0:00 Defining the Endocrine System
- 1:15 Male and Female Glands
- 2:43 Lesson Summary
Endocrine System Function
The main function of the endocrine system is to regulate and monitor the levels of hormones circulating in the blood. This is because the endocrine system produces hormones that can regulate moods, growth, metabolism, development, and reproduction, which are released in accordance to what the body needs. One gland, the pituitary gland, is primarily responsible for sensing when hormone levels are increased and relays information to the other glands to stop producing the hormones. The pituitary gland can also sense when hormone levels are too low and instruct other glands to start producing more hormones.
Hormones affect several processes in the body, such as:
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Parts of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system consists of several parts, including the major glands that make up this network. They include the hypothalamus, the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, and adrenal glands, and the pancreas.
Hypothalamus
Located in the middle part of the brain, the hypothalamus is responsible for regulating and controlling the endocrine system. It combines information from the nervous system and the other glands of the endocrine system in order to regulate which hormones should be produced. The hypothalamus is intimately connected to the pituitary gland, which is the gland responsible for producing the hormones. The hypothalamus controls several processes, including sleep, mood, hunger, thirst, and sexual function.
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized component of the endocrine system that produces the hormones that controls other glands, such as the thyroid and adrenal glands, in addition to testes and ovaries. In fact, the pituitary gland signals the sex glands to release the hormones when the body reaches a certain age. It is also located in the brain, and mediates bodily functions like blood pressure, water balance, and how the body develops.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
How Does the Endocrine System Work?
The endocrine system works by continuously monitoring the level of hormones in the blood, essentially having a pivotal role in the body’s homeostasis, which is the steady balance of conditions and processes in the body. This corresponds to metabolic balance in the body, and is important for optimal bodily functioning. The endocrine system achieves this by regulating several processes, including cellular metabolism; homeostasis of sugar and other key nutrients; and regulation of blood pressure and heart rate, sleep, digestion, and sexual development.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Lesson Summary
The endocrine system is an essential network in the body that consists of glands, which are organs that produce chemicals known as hormones that travel to target sites on cells, organs, and tissues. Key functions include metabolism, sleep, temperature, blood pressure, and development.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Male and Female Glands
Difficulties with any of these glands can lead not just to health problems, but also to long-term changes in behavior. They can affect moods and the choices we make.
Male and female sex glands are also part of the endocrine system. If you’re a guy, your testes produce the male sex hormones testosterone. If you’re a girl, your ovaries produce the female sex hormones estrogen. Changing hormone levels are responsible for the physical and emotional changes that occur when you hit puberty.
The pituitary gland in your brain is called the ‘master gland’ because it secretes hormones that trigger your other glands. It regulates the amount of hormones released by your thyroid, adrenal glands, and sex glands. It’s the command center that controls your body’s growth, and signals your ovaries or testes to make testosterone or estrogen.
Lesson Summary
You’ve learned about the hormone-secreting glands that make up your endocrine system. Major glands include the pituitary gland in your brain, the thyroid gland in your neck, the adrenal glands and pancreas in your belly, and your reproductive glands (your testes or ovaries). Hormones affect your behavior and bodily functions in many ways. Think of your hormones at work the next time you feel grumpy from low blood sugar levels or after recovering from a sudden scare…BOO!
Defining the Endocrine System
Teenagers aren’t the only ones with hormones. And hormones don’t just cause mood swings.
The hormones of your endocrine system help to regulate your energy levels, growth, emotions and ability to reproduce. Hormone-producing glands make up your endocrine system. Hormones are chemicals that your body produces to tell your cells how to behave. They can regulate growth and energy consumption.
Your thyroid gland is in your neck. Your thyroid regulates your metabolism, or how fast your body uses energy. Low levels of thyroid hormones may make you feel tired and lead to weight gain. But, if you have a hyperactive thyroid, your heart may race and you may feel jittery and have trouble falling asleep.
Your pancreas is a gland in your belly that also affects your energy levels. Your thyroid controls the rate at which your body uses energy, and your pancreas regulates how much energy your body gets. Your pancreas produces insulin , the hormone that helps your body absorb sugar in your bloodstream to give it energy. You feel sluggish in the morning when you have low blood sugar. Once you eat breakfast, sugar from the food is carried by your blood. Insulin from your pancreas helps your cells take in the sugar that fuels your body.
In your belly, you also have adrenal glands, which rest on top of your kidneys. Your adrenal glands pump out adrenaline hormones when you’re faced with stress or excited. Say you’re driving, and suddenly see a baby in the road. Your nervous system sends signals to the glands in your endocrine system to put your reactions in motion. Your adrenal glands in your endocrine system release adrenaline to trigger a reaction. You get scared and react quickly as you slam on the brakes. You laugh when you realize it was just a doll that someone lost!
Male and Female Glands
Difficulties with any of these glands can lead not just to health problems, but also to long-term changes in behavior. They can affect moods and the choices we make.
Male and female sex glands are also part of the endocrine system. If you’re a guy, your testes produce the male sex hormones testosterone. If you’re a girl, your ovaries produce the female sex hormones estrogen. Changing hormone levels are responsible for the physical and emotional changes that occur when you hit puberty.
The pituitary gland in your brain is called the ‘master gland’ because it secretes hormones that trigger your other glands. It regulates the amount of hormones released by your thyroid, adrenal glands, and sex glands. It’s the command center that controls your body’s growth, and signals your ovaries or testes to make testosterone or estrogen.
Lesson Summary
You’ve learned about the hormone-secreting glands that make up your endocrine system. Major glands include the pituitary gland in your brain, the thyroid gland in your neck, the adrenal glands and pancreas in your belly, and your reproductive glands (your testes or ovaries). Hormones affect your behavior and bodily functions in many ways. Think of your hormones at work the next time you feel grumpy from low blood sugar levels or after recovering from a sudden scare…BOO!
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account