Endocrine system notes pdf
- Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, _________________________
- Regulation of growth, metabolism, and ______________________________
- Responses to ________________________________
- Maintains _____________________________________
Major Structures & Location
1. Pineal
2. Pituitary
3. Thyroid & Parathyroid
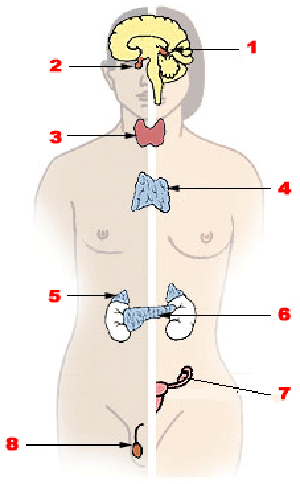
4. Thymus
5. Adrenals
6. Pancreas
7. Ovary
8. Testes
Control of Hormonal Secretions – Negative versus Positive Feedback
When the levels go above or below a _______________________, the endocrine system secretes hormones to lower or raise the level.
Positive Feedback
Example:
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
Prolactin or PRL –
Growth hormone or GH
Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH –
Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH -.
Luteinizing hormone or LH –
Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
Antidiuretic hormone or ADH –
The thyroid hormones control your _________________________, which is the body’s ability to break down food and store it as energy
Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) – increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates
Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium
Goiter
Hypothyroidism (cretinism)
Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease)
Cancer
Located behind the thyroid, four tiny glands that help maintain calcium and phosphorous levels
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) – takes calcium from the bones to make it available in the blood
Adrenal Glands Located above each kidney.
Adrenal Cortex = ______________ area Medulla = ______________
Adrenal glands produce _______________________________
Large gland behind stomach, maintains healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels.
Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin
Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ______________________________________
Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the ____________________ of glucose by cells
Diabetes Mellitus –insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hyperglycemia) and excess is excreted in the urine
Pineal Gland – secretes melatonin which maintains _____________________________
Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to ______________________
Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries – testosterone, progesterone, estrogen
What is gonadotropin?