The endocrine system and hormones
The endocrine system is a group of glands and cells in the body that make hormones and release them into the blood. Hormones are natural substances that act like chemical messengers between different parts of the body. They control many functions including growth, reproduction, sexual function, sleep, hunger, mood and metabolism . Certain cells in the body have proteins called receptors that react to a hormone. How the cell responds depends on which hormone it is reacting to.
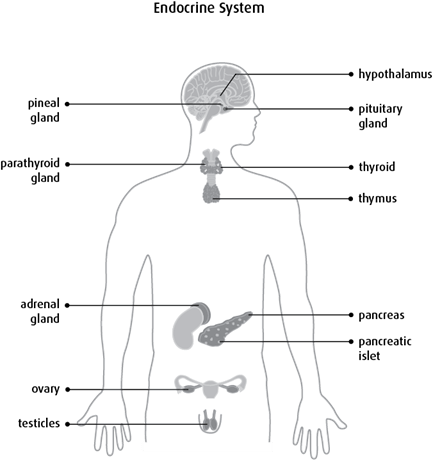
There are many organs and glands that make up the endocrine system.
Pituitary gland
- growth
- metabolism
- the making of breast milk after giving birth
- menstruation, maturing eggs and the making of estrogen by the ovaries in women
- the making of sperm and testosterone by the testicles in men
- steroid levels in the body
The hormones made by the pituitary gland also cause other endocrine glands to make or stop making other hormones. Together, the pituitary gland and hypothalamus control the endocrine system and hormone levels in the body.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is an important part of the brain and has many jobs controlling different parts of the body. One of the jobs of the hypothalamus is to make hormones, including those that control the pituitary gland and control blood pressure. The hypothalamus reacts to changes in hormone levels in the body.
Pineal gland
The pineal gland is a tiny gland deep in the brain that makes the hormone melatonin, which controls sleep patterns.
Thyroid
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck in front of the upper part of the windpipe (trachea). The thyroid makes hormones that control many body functions including growth and metabolism. It also makes a hormone that controls the amount of calcium in the body.
Parathyroid gland
The parathyroid glands are 4 small glands attached to the back of the thyroid. They make and release parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone helps control calcium levels in the blood. Most calcium is stored in the bones. When calcium levels in the blood are low, the parathyroid glands make PTH to get the bones to release calcium into the blood. When calcium levels in the blood are high, the parathyroid glands make less PTH, and calcium levels in the blood lower.
Thymus
The thymus is a gland in the upper part of the chest, just behind the breastbone (sternum) and between the lungs. The thymus is part of the endocrine system, the lymphatic system and the immune system. The thymus makes hormones that help T cells (a type of white blood cell) to mature and function.
Adrenal glands
We have 2 adrenal glands, one on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands make several hormones that control different body functions, including metabolism, heart rate, blood pressure and water and salt balance. They also make small amounts of the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone.
Pancreas
The pancreas is a slim, long organ in the upper left part of the abdomen that sits under the stomach between the liver and spleen. The pancreas is part of the digestive and endocrine systems. The pancreas makes enzymes that are released directly into the small intestine to help digest food. It also makes hormones that help with digestion and control blood sugar (glucose) levels (such as insulin). The hormones are made in small groups of specialized cells in the pancreas called islets. This part of the pancreas that makes hormones is called the endocrine pancreas.
Ovaries
The ovaries are part of a woman’s reproductive system (female reproductive system). Women have 2 ovaries where immature eggs develop into mature eggs (ova). The ovaries also make the hormones estrogen and progesterone. The ovaries are deep inside a woman’s pelvis, on both sides of the uterus (womb) close to the ends of the fallopian tubes.
Testicles
The testicles (testes) are a part of a man’s reproductive system (male reproductive system). A man has 2 testicles. The testicles make sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone.
Neuroendocrine system and neuroendocrine cells
The neuroendocrine system is made up of special cells called neuroendocrine cells. They are scattered throughout the body. Neuroendocrine cells act like nerve cells (neurons) and also make hormones like cells of the endocrine system (endocrine cells). Neuroendocrine cells receive messages (signals) from the nervous system and respond by making and releasing hormones.
Neuroendocrine cells are scattered along the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and are found in the gallbladder, lungs, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid glands, pancreas and inner layer of the adrenal gland (adrenal medulla).