Functions of Endocrine Gland
How many of you experience various hormonal changes? Almost all of us! Isn’t it? But, why do these changes happen? Who secretes these hormones? In this chapter, we will look at the Functions of Endocrine Gland, the hormones they secrete and so on.
Suggested videos
Endocrine System
Before we proceed with the topic, do you know who the mastermind behind these hormones is? Let us first see that. Yes! The endocrine system is the main system to control all the development of hormones in our body. The endocrine system is comprised of nine primary glands. These glands produce hormones. There are many other organs that provide secondary functions such as processing the secretions to trigger bodily function of endocrine gland.
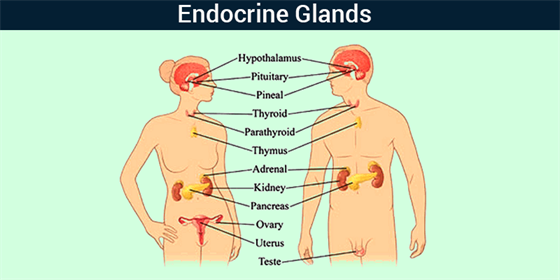 Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
So, what are endocrine glands? Endocrine glands are important glands of the endocrine system. They secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood rather than through a duct. The endocrine glands belong to the body’s control system. The hormones which they produce help to regulate the functions of both cells and tissues throughout the body. the various types of major endocrine glands include:
- Pituitary gland (Hypophysis)
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid glands
- Adrenal glands
- Pancreas
- Gonads
- Pineal gland
These glands produce different types of hormones. These hormones induce a different and a specific response in other cells, tissues, and also the organs that are located throughout the body. We will now look at each of these glands in brief and understand their primary functions.
Browse more Topics under Reaching The Age Of Adolescence
Pituitary gland (Hypophysis)
The pituitary gland hangs from the base of the brain by a stalk. It is enclosed and also protected by a bone. It consists of a hormone-producing glandular portion and a neural portion.
The pituitary gland is the master gland. This is pea-sized and is located at the bottom of the brain. They control and regulate other glands in the body. Hormones released by this gland are growth hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, Luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and so on.
Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is located in the anterior throat. Thyroid follicles store colloid containing thyroglobulin, a glycoprotein from which thyroid hormone is derived.
Parathyroid glands
The parathyroid glands are located on the back of the thyroid gland. These are primarily responsible for causing an increase in blood calcium levels by targeting bone, the intestine, and the kidneys.
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are located above the kidneys in humans and in front of the kidneys in other animals.
Pancreas
The pancreas is located in the abdomen and is close to the stomach. It is both an exocrine and an endocrine gland.
Gonads
The ovaries of the female which is located in the pelvic cavity release two main hormones. While the testes of the male begin to produce testosterone at puberty in response to Luteinizing hormone.
Pineal gland
The pineal gland is located in the diencephalon. The primary hormone of this gland is melatonin. It influences the daily rhythms and may also have an anti-gonadotropic effect in humans. It also regulates the wake-up and sleep clock and also helps in immunity.
Solved examples for You
Question: Mention the function of thyroid glands.
Answer: The thyroid gland is present in front of the neck. It releases the hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They regulate the body metabolism. Iodine is vital for thyroxine synthesis. Its deficiency leads to causing goitre.