Glands and Hormones in Human Body (ग्रन्थियाँ)
General Science – Biology topic – “Glands and Hormones in Human Body (ग्रन्थियाँ)”, is important for all competitive exams like CET, Tire II of SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and for other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic- Glands and Hormones in Human Body (ग्रन्थियाँ):
Glands and Hormones in Human Body
(ग्रन्थियाँ और हार्मोन)
Glands are important organs located throughout the body. They produce and release substances, called Hormone that perform certain functions. All glands in human body are divided into two systems:
Endocrine and Exocrine glands serve very different purposes in the body.
The Endocrine System
अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियां (Endocrine glands)
The endocrine system is made up of the endocrine glands. These are the glands that secrete their product (Hormones) directly into the blood. There are no ducts in endocrine glands. These hormones control a number of important functions in our body, such as:
- our growth and development
- metabolism
- mood
- reproduction
- The endocrine system regulates how much of each hormone is released.
( Note: – Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers. They carry information and instructions from one set of cells to another).
Although there are endocrine glands scattered throughout the body, they are still considered to be one system because they have similar functions, similar mechanisms of influence, and many important interrelationships.
Some organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and heart, produce hormones, but their primary function is not hormone secretion.
Our endocrine glands include:
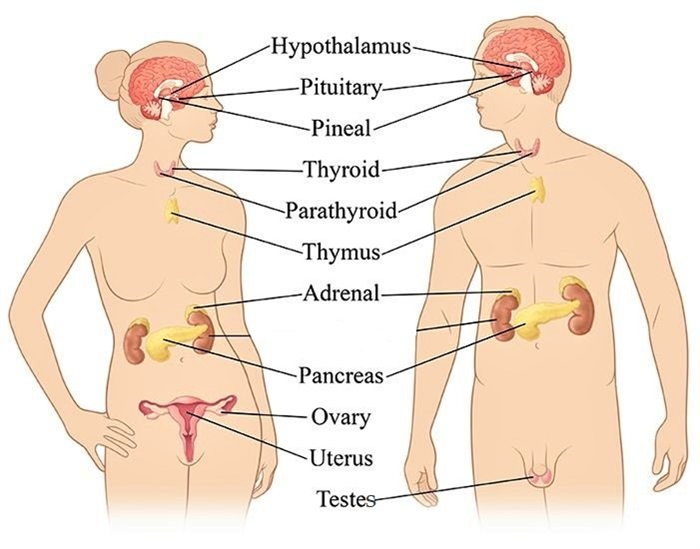
Many glands make up the endocrine system. The hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland are in our brain. The thyroid and parathyroid glands are in our neck. The thymus is between our lungs, the adrenals are on top of our kidneys, and the pancreas is behind our stomach. Ovaries (if you’re a woman) or Testes (if you’re a man) are in our pelvic region.
As many parts of the body make hormones, the major glands that make up the endocrine system are the:
- Hypothalamus (हाइपोथेलेमस)
- Pituitary (पीयूष ग्रन्थि)
- Pineal Gland (पीनियल ग्रंथि)
- Thyroid (अवटु ग्रन्थि)
- Parathyroid (पराअवटु ग्रंथि)
- Thymus gland (अवस्थित ग्रंथि)
- Adrenals (अधिवृक्क ग्रन्थि)
- Pancreas (अग्न्याशय)
The hypothalamus is in the lower central part of the brain. It links the endocrine system and nervous system. The hypothalamus functions as a communication center for our pituitary gland, sending signals and messages to the pituitary to produce and release hormones. Its main job is to tell our pituitary gland to start or stop making hormones.
Our hypothalamus influences a number of our body’s functions, including:
The pituitary gland is a pea size gland at the base of our brain, just behind the bridge of our nose. It’s controlled by the hypothalamus, which sits just above it. The pituitary gland is often called the “Master gland” because it controls a number of other hormone glands, including the:
The pituitary gland makes many hormones, such as:
- Growth hormone(STH): This growth hormone controls the development of bones and muscles. A person having a deficiency of growth hormone becomes very short and the person having too much growth hormone becomes very tall.
- Prolactin(LTH): which activates milk production in women who are breastfeeding
- Thyrotropin(TSH): which stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones
- Antidiuretic hormone: which helps control body water balance through its effect on the kidneys
- Oxytocin: which triggers the contractions of the uterus that happen during labor pain/child birth.
- Luteinizing hormone: which manages oestrogen in women and testosterone in men.
Note: The pituitary also secretes endorphins chemicals that act on the nervous system and reduce feelings of pain. The pituitary also secretes hormones that signal the reproductive organs to make sex hormones.
Our pineal gland is located deep in the center of our brain. Its function is not completely understood, but we do know that it secretes and regulates certain hormones, including melatonin.
Thyroid gland is located in the front of our lower neck, just below our larynx. It has a shape similar to a butterfly. It secretes hormones that affect virtually every tissue in our body.
The thyroid gland makes hormones called thyroxin and triiodothyronine which contain iodine. The function of these hormones is to control the rate of metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the body. The deficiency of iodine in the diet can cause a deficiency of thyroxin hormone in the body. This causes a disease called a goitre.
Thyroid hormones regulate our metabolism, heart, and digestive function. They also play a role in our brain and nerve development, muscle control, and mood.
Attached to the thyroid, there are four tiny glands that work together called the parathyroids. The parathyroid gland secretes a hormone called parathormone which helps to regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which the thyroid makes.
- Parathyroid hormones: Release when there is deficiency of calcium in blood.
- Calcitonin hormones: It control quantity of calcium in blood.
This gland is present in the lower part of the neck and upper part of the chest. Thymus gland secretes thymus hormone which helps in the development of the immune system of the body. This gland makes white blood cells called T-lymphocytes that fight infection and are crucial to develop child’s immune system. The thymus starts to shrink after puberty (यौवन अवस्था).
Adrenal glands (triangular shaped) are located at the top of each kidney. This gland is also called glands of emergency. This gland have two major parts – Adrenal medulla and Adrenal Cortex. In absence of Adrenal cortex a person can die within one or two week due to Adison disease. Adrenal glands produce various hormones, some of which include:
The inner part of the adrenal gland (adrenal medulla) produce Adrenaline hormone which is also known as “fight or flight (उडो और लड़ो)” hormone. This hormone is secreted in large amounts when the person is excited or frightened. It increases blood pressure and heart rate when the body is under stress.
The outer part of the adrenal gland (adrenal cortex) produce it that help to control salt and water balance in the body, the body’s response to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development and function.
The pancreas — a long, flat organ located in our abdomen and secretes two main hormones called insulin and glucagon which are hormones that control the level of glucose, or sugar, in the blood. The function of insulin is to lower the blood sugar level. The deficiency of insulin hormone causes a disease called diabetes. A person having diabetes has large quantities of sugar in the blood.
Reproductive Glands (Gonads):
The gonads are the main source of sex hormones. Most people don’t realize it, but both guys and girls have gonads.
Male gonads are known as testes. They secrete hormones called androgens the most important of which is testosterone. The testosterone controls the development of male sex organs and male features such as deeper voice, mustache, beard, making of sperm etc.
Female gonads known as the ovaries. They make eggs and secrete the female hormones estrogen (oestrogen) and progesterone.
-
- Estrogen helps in controlling the development of female sex organs and female features such as feminine voice, soft skin, body fat around the hips and thighs, breast growth during the puberty.
- The progesterone hormone controls the uterus changes in the menstrual cycle. It helps in the maintenance of pregnancy.
Exocrine System
बहिःस्रावी ग्रंथियाँ (Exocrine glands)
Exocrine glands produce other substances — not hormones that are released through ducts to the exterior of our body, such as sweat, saliva, and tears. The salivary gland secretes the saliva into the salivary duct.
The substances released by our exocrine glands play important roles in our body like body temperature regulation, protect our skin and eyes, and even help mothers feed babies by producing breast milk.
Note: Lymph nodes are often referred to as glands, but they’re not true glands. They’re part of our immune system and help our body fight against infection.
Salivary glands are located in our mouth. Hundreds of small glands located throughout our tongue, palate, lips, cheeks etc
We have three pairs of major salivary glands, including the:
- Parotid glands: located in front of and just below our ears.
- Sublingual glands: located just under your tongue.
- Submandibular glands: located below your jaw.
Salivary glands produce saliva and empty into our mouth through ducts. Saliva serves a few important purposes, including moistening our food to help in chew, swallow, and digest it. Saliva also contains antibodies that kill germs.
Sweat glands:
It is also known as sudoriferous glands. Our skin is contains two types’ sweat glands:–
- Eccrine: Eccrine glands open directly onto our skin and regulate our body temperature by releasing water to the surface of our skin when our body temperature rises.
- Apocrine: Apocrine glands open into the hair follicle and are found in hair-bearing areas, such as the skin, armpits, and groin. These glands secrete a milky fluid, usually as a response to stress. Our body also contains modified apocrine glands: on the eyelids, on areola and nipples, in the nose and ears.
Sebaceous glands are located throughout our skin like – on our hands and feet but not on our palms and soles. They secrete an oily substance called sebum that lubricates our skin.
These glands perform a few functions in our body, such as:
Mammary glands, which are a type of sweat gland, are responsible for the production of breastmilk. Males also have glandular tissue in the breasts, but oestrogen (estrogen) produced during puberty triggers the growth of this tissue in females.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy signal the ducts to produce milk in preparation for the baby.
The lacrimal gland (tear gland) is an exocrine gland located above the eyeball, in the anterior part of the upper outer aspect of each orbit. It secretes lacrimal fluid (tear fluid).
There are some glands that have both exocrine and endocrine functions. Pancreas, testes, and ovaries perform both exocrine and endocrine functions. For example, the pancreas acts as an endocrine gland and secretes insulin. It also acts as an exocrine gland and secretes pancreatic juice into the pancreatic duct.
Some Important facts about Glands and Hormones for Competitive Exams:
- Smallest and most important gland of human body:pituitary gland.
- Largest gland of human body : Pancreas (in stomach)
- Gland that secrete tears : lacrimal gland
- Harmon responsible for growth produced by: pituitary gland.
- Gland that produce Oxytocin hormone: pituitary gland.
- Life saver hormone is: Adrenaline hormone
- “ fight or flight (उडो और लड़ो) ” hormone is called to : Adrenaline hormone
- Gland that is known as glands of emergency: Adrenal glands.
- Pacemaker of endocrine glands is: Thyroxin hormones.
- Insulin secrete by: beta cells (β) of pancreas.
- Hormone that is responsible for calcium and phosphate in blood: Parathyroid hormones.
- Gland responsible for breastmilk: Mammary glands.
If you like and think that Biology topic on “Glands and Hormones in Human Body (ग्रन्थियाँ)” is helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.