The Anatomy and Physiology of Animals/Endocrine System Worksheet/Worksheet Answers
1. Fill in the gaps in the sentences below using the words in the list.
target; blood system; ducts; hormones a. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the blood. In other words they have no ducts. b. Endocrine glands secrete chemicals called hormones. c. Hormones are transported from the endocrine glands to all parts of the body by the blood system. d. Although hormones are carried throughout the body they only affect specific target organs and tissues
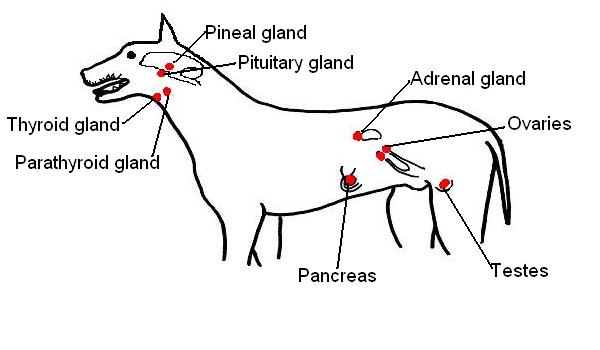
2. The position of endocrine organs have been indicated in red on the diagram of a composite male and female dog shown below. Add the labels in the list to the diagram.
Ovary; Pancreas; Thyroid gland; Pituitary gland; Testis; Adrenal gland; Pineal gland; Parathyroid gland
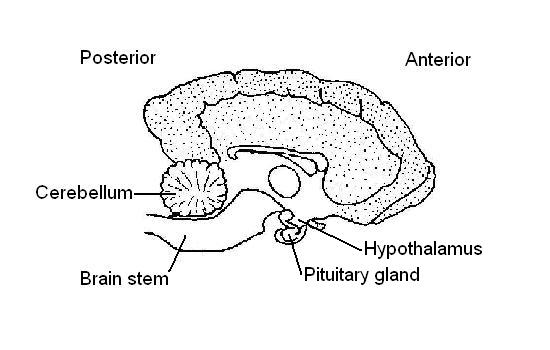
3. On the diagram of the brain below indicate the position of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland.
4. In the table below list 3 hormones produced by the pituitary gland and state the function of each.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| 1.Growth hormone. | Stimulates growth of the body by increase in length of the long bones |
| 2.Oxytocin | Stimulates milk “let down” |
| 3.Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) | Stimulates the development of the ovarian follicle. |
| Plus: Luteinising hormone(LH) | Stimulates development of the corpus luteum of the ovary |
| Plus: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) | Stimulates the production of concentrated urine |
| Plus some others |
5. Fill in the following table with the endocrine organ the hormones are produced by.
| Hormone | Produced by: |
|---|---|
| Insulin | Pancreas |
| Progesterone | Corpus luteum |
| Oestrogen | Ovarian follicle |
| Growth hormone | (Anterior) pituitary gland |
| Adrenaline | Adrenal medulla |
| Antidiuretic hormone | (Posterior) pituitary gland |
| Testosterone | Testis |
| Aldosterone | Adrenal cortex |
| Melatonin | Pineal gland |
| Oxytocin | (Posterior) pituitary gland |
| Thyroxine | Thyroid gland |
6. Match the hormones in the list below with their functions.
Oxytocin; Insulin; Oestrogen; Growth hormone; Antidiuretic hormone; Testosterone; Adrenaline; Cortisone; Melatonin; Progesterone; Thyroxine; Luteinising hormone; Follicle stimulating hormone
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) | 1. Stimulates development of the ovarian follicle. |
| Oxytocin | 2. Stimulates milk “let down”. |
| Insulin | 3. Controls blood glucose levels. |
| Thyroxine | 4. Influences the rate of growth and development of young animals. |
| Growth hormone | 5. Stimulates the growth of long bones. |
| Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) | 6. Stimulates absorption of water from the kidney tubule. |
| Melatonin | 7. Influences the development of sexual maturity. |
| Luteinising hormone (LH) | 8. Stimulates the development of the corpus luteum. |
| Oestrogen | 9. Stimulates the development of female sexual characteristics. |
| Testosterone | 10. Stimulates the development of the male sexual characteristics. |
| Cortisone | 11. Affect glucose, protein and fat metabolism. |
| Progesterone | 12. Prepares the lining of the uterus for pregnancy. |
| Adrenaline | 13. Prepares the body for emergency situations. |
1. melatonin; oxytocin; growth hormone; antidiuretic hormone; follicle stimulating hormone. Melatonin is the only hormone in the list not produced by the pituitary gland. 2. progesterone; oestrogen; luteinising hormone; cortisone; follicle stimulating. Cortisone is the only hormone in the list not involved in any major way with reproduction. 3. adrenaline; cortisone; aldosterone, oestrogen, insulin. Insulin is the only hormone in the list not produced by the adrenal gland.